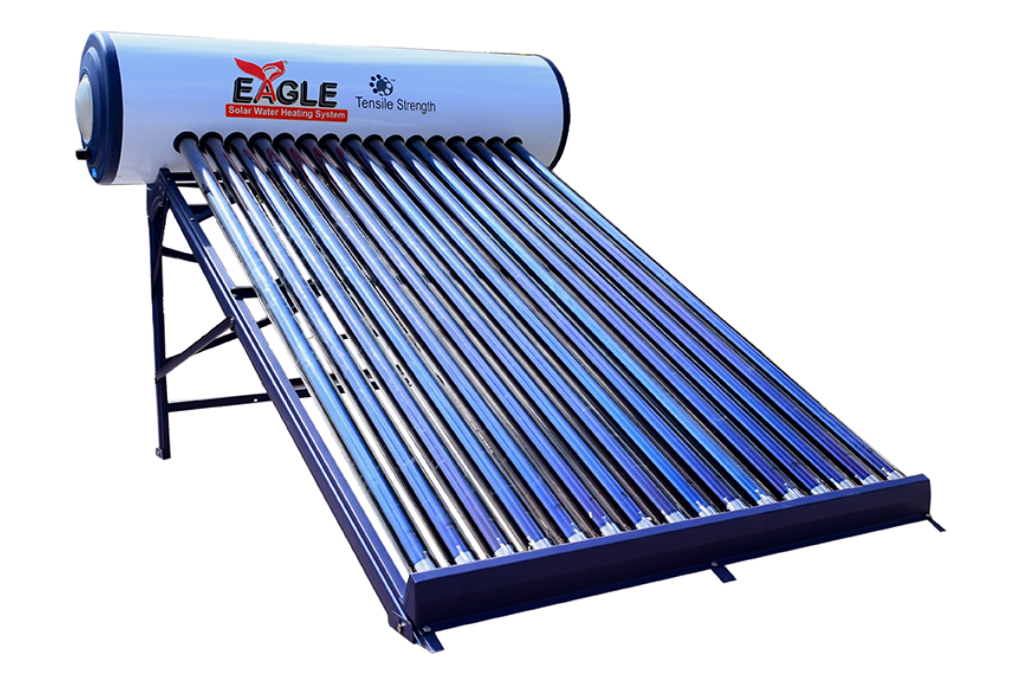
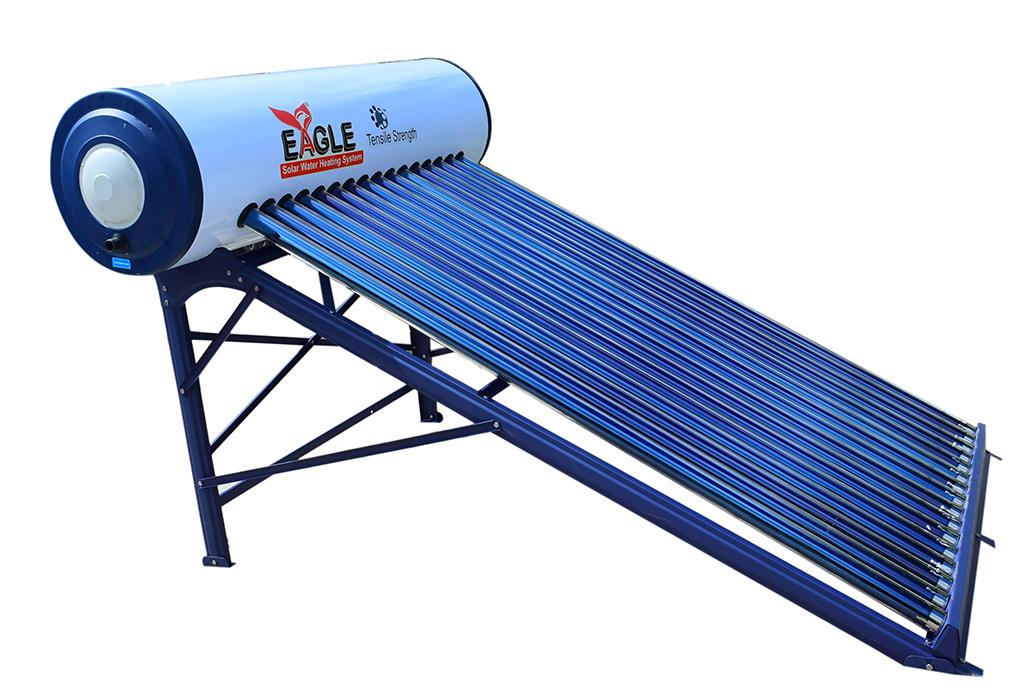
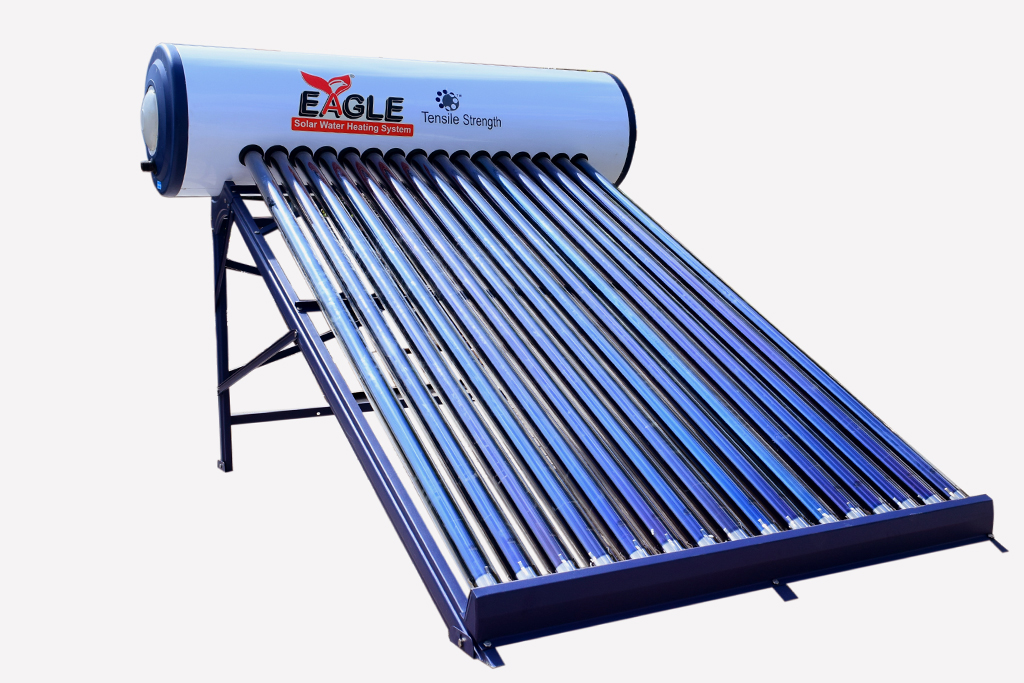
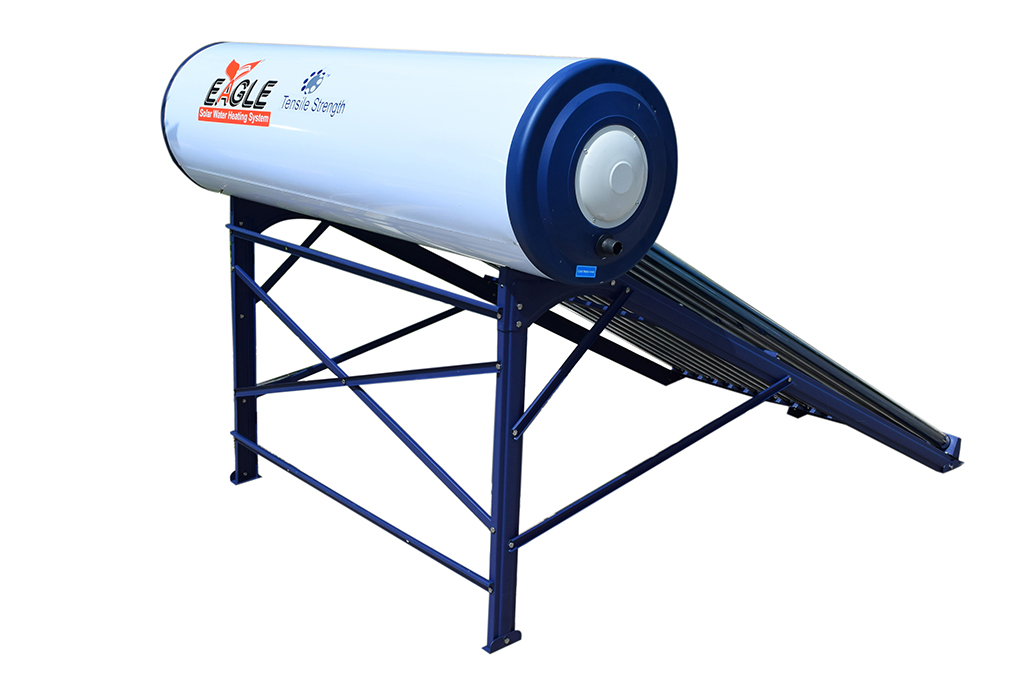
Glass Coated Solar Water heater
Glass Line - The future of Solar Water Heating in India
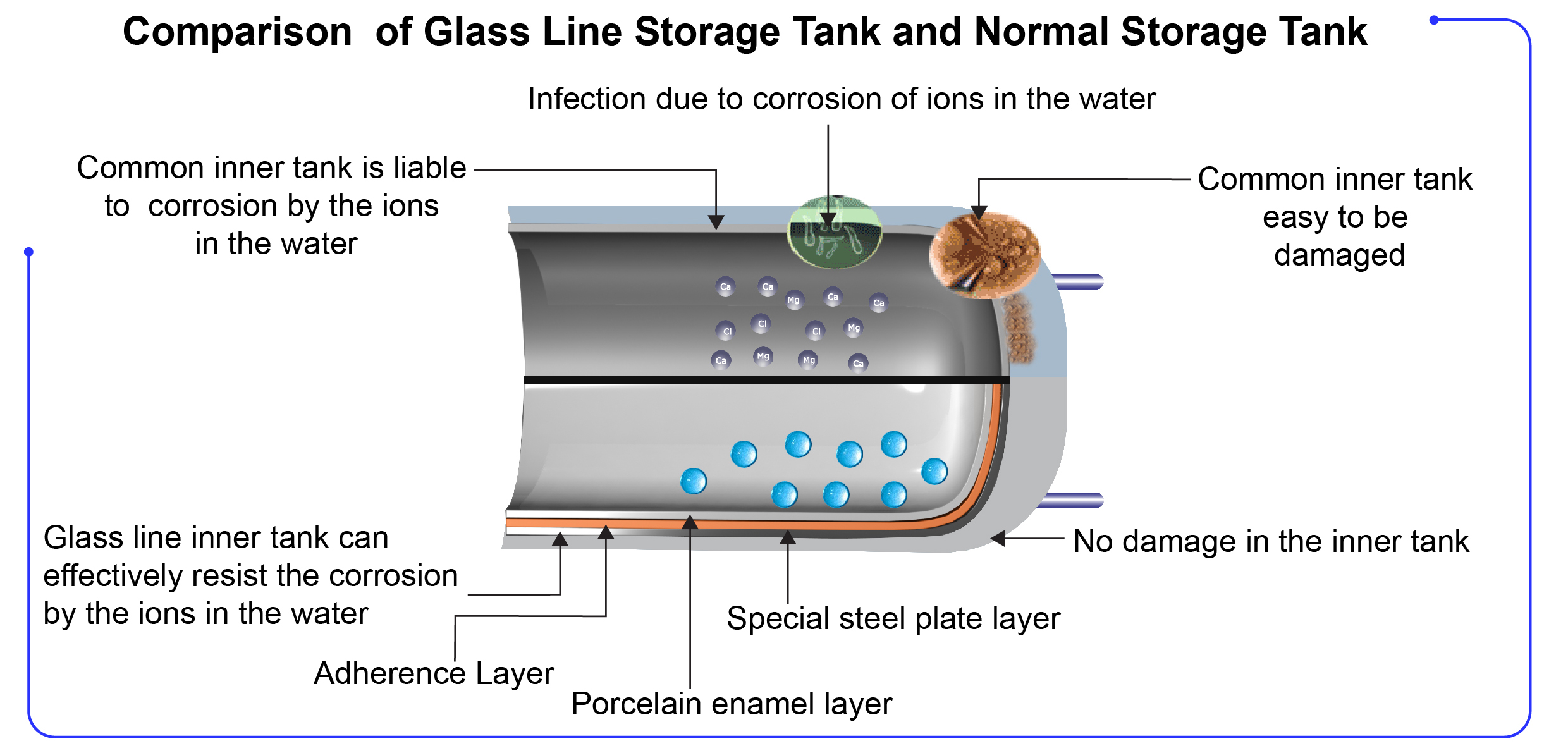
Industrial porcelain enamel (also known as glass lining, glass-lined steel, or glass fused to steel) is the use of porcelain enamel (also known as vitreous enamel) for industrial, rather than artistic, applications. Porcelain enamel, a thin layer of ceramic or glass applied to a substrate of metal, is used to protect surfaces from chemical attack and physical damage, modify the structural characteristics of the substrate, and improve the appearance of the product.
Enamel has been used for art and decoration since the period of Ancient Egypt, and for industry since the Industrial Revolution. It is most commonly used in the production of cookware, home appliances, bathroom fixtures, water heaters, and scientific laboratory equipment.
The most important characteristic of porcelain enamel, from an industrial perspective, is its resistance to corrosion. Mild steel is used in almost every industry and a huge array of products; porcelain enamel is a very economic way of protecting this, and other chemically vulnerable materials, from corrosion. It can also produce very smooth, glossy finishes in a wide array of colours; these colours will not fade on exposure to UV light, as paint will. Being a fired ceramic, porcelain enamel is also highly heat-resistant; this allows it to be used in high-temperature applications where an organic anti-corrosion coating or galvanization may be impractical or even dangerous.
The application of industrial porcelain enamel can be a complicated process involving many different and very technical steps. All enamelling processes involve the mixture and preparation of frit, the unfired enamel mixture; the preparation of the substrate; the application and firing; and then finishing processes. Most modern applications also involve two layers of enamel: a ground-coat to bond to the substrate and a cover-coat to provide the desired external properties.